
Safari generally provides the fastest and most efficient browsing experience for Mac users. Apple puts a lot of work into optimizing the browser’s performance and energy consumption specifically for Apple hardware.
Unfortunately, this doesn’t always hold up over time. Safari can become slow, bloated, and unresponsive like any other browser. Let’s take a look at some of the common causes (and solutions) for a sluggish Safari.
1. Update and Restart Your Mac

Restarting your computer fixes so many of life’s problems, not least a lagging browser. It should always be a first troubleshooting step for such issues, along with running any outstanding minor updates (which you can find under App Store > Updates).
2. Close Unneeded Tabs

How many tabs do you have open right now, and how many of those tabs do you really need? Safari will keep many of your tabs active in the background, even if you’re not using them. One of the easiest ways of speeding up Safari is to simply close some tabs.
If you’re particularly protective of your browser session, try an extension like Sessions. This allows you to save all your open tabs for later recall, so you can close everything you aren’t using right now.
3. Clear Cache and Temporary Files
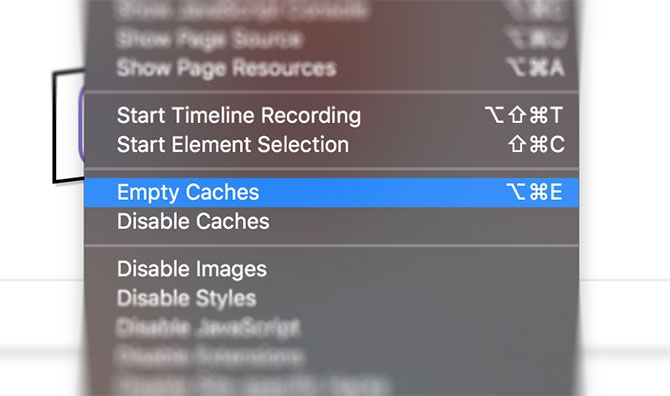
Like almost all browsers, Safari keeps a cache of visited pages and associated data. This takes up space on your disk, which can contribute to performance problems. It’s always a good idea to blow away Safari’s cobwebs once in a while, particularly if you’re having performance issues.
To clear your Safari cache:
- Launch Safari and click Safari > Preferences in the menu bar at the top of the screen.
- Click on the Advanced tab, then check Show Develop menu in menu bar at the bottom of the window.
- Close the Preferences window and then click Develop > Empty Caches in the menu bar at the top of the screen.
4. Disable Thirsty Extensions

Safari has no shortage of extensions, but they can do more harm than good by slowing everything down. This is particularly true for extensions that directly affect the browsing experience. A good example is TamperMonkey, which can change how websites appear and behave with user scripts.
To isolate extension-related slowdown, try disabling all your extensions under Safari > Preferences > Extensions. To disable an extension, uncheck the checkbox next to its name. You can then try re-enabling extensions one by one to find the culprit.
Disabling extensions in this manner doesn’t remove them. You’ll need to click the Uninstall button under each entry on the Extensions tab to completely remove an extension.
5. Restrict Greedy Plugins

Plugins, like Adobe Flash or Unity Player, should also be kept on a short leash. To maintain optimal browser speed, you should set plugins to Ask you before they run. You can configure this behavior under Safari > Preferences > Security > Plug-in Settings.
You can disable any plugins you’re not using by unchecking the checkbox next to its name. Safari lets you configure default behavior for any websites you currently have open from the list. Set the default behavior for all other websites in the When visiting other websites dropdown menu.
Plugins that can run without restriction will slow down your browsing experience. By restricting plugins, your browser will favor modern web technologies such as HTML5 over outdated and insecure plugins like Flash.
6. Upgrade macOS
Yearly macOS revisions bundle new major versions of Safari. If you don’t install the latest version of macOS, you won’t have the latest version of Safari. Apple will patch older versions with security fixes and other improvements, but the latest and greatest features require a macOS update.
New versions of Safari mean better compatibility with the latest web technologies. Apple’s tweaking under the hood often results in faster rendering times and a speedier browser experience overall.
There’s also something to be said for upgrading your operating system, since many underlying issues with your system will be patched up along the way.
7. Identify Dodgy Websites and Crashed Tabs
Sometimes Safari can slow to a crawl as a result of a single problematic website. Websites can crash for all sorts of reasons, including too many scripts, auto-playing advertisements, rogue extensions, and malfunctioning embeds. Occasionally, this can bring your whole Mac to a grinding halt.
Sometimes these pages consume more than their fair share of resources, and other times they crash entirely and leave you with the spinning pinwheel of death. To rectify the situation:
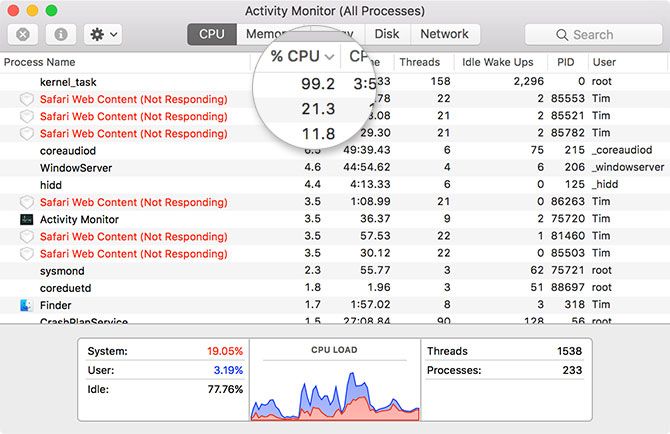
- Launch Activity Monitor under Applications > Utilities (or just use Spotlight).
- On the CPU tab click on the % CPU column to arrange running processes by processing power.
- Select any thirsty websites or tabs that have crashed, then click on the X button in the top-left to kill the process.
- Confirm that you want to quit the process, and repeat as necessary for any other problem tabs.
8. Not Enough Free Space
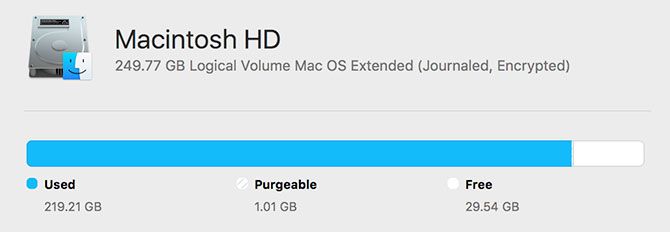
A lack of free space on your Mac can have devastating consequences for your overall performance. A Mac with limited free space is more likely to freeze, stutter, and crash. This can cause your whole system to run slowly, but Safari is often one of the first apps to buckle as individual resource-intensive tabs become unresponsive.
For best results, maintain a healthy buffer of free space of 10GB or greater. Follow our tips for freeing up space on your Mac and consider expanding your MacBook’s storage if you run out of options.
9. Other macOS-Related Performance Issues
Boosting overall system performance will boost overall browser performance. Less resources tied up in non-critical tasks means more resources available for web browsing purposes.
First make sure you’re not making any mistakes that might slow down your Mac. Remove applications you don’t need from starting up under System Preferences > Users > Login Items. Close resource-intensive background apps like Photoshop or Final Cut Pro.
10. Check for Network Connection Problems
If your internet connection is slow, Safari will be slow. To isolate connection problems, test your internet connection speed to see if that’s to blame.
Changing your DNS settings can improve your internet speed, which is worth a try if you’re having persistent connection problems. It’s also worth keeping a secondary browser installed—like Chrome or Firefox—for those stubborn websites that aren’t optimized for Apple’s browser.
Read the full article: 10 Safari Browser Tips for Boosting Speed and Performance


