One of the most frustrating Windows issues is slow startup. When Windows takes forever to boot, you dread turning on or rebooting your computer. Certain Windows 10 versions are especially prone to this.
Thankfully, slow booting is a solvable issue. We’ll show you the most common fixes for slow startup times in Windows 10.
1. Disable Fast Boot
By far, the most problematic setting when it comes to boot time in Windows 10 is the Fast Startup option. This is enabled by default, and is supposed to reduce startup time by pre-loading some boot information before your PC shuts off.
While the name sounds promising, it’s caused issues for a lot of people. Thus, it’s the first step you should try when you have slow boot problems. (Note that restarting your computer isn’t affected by this feature.)
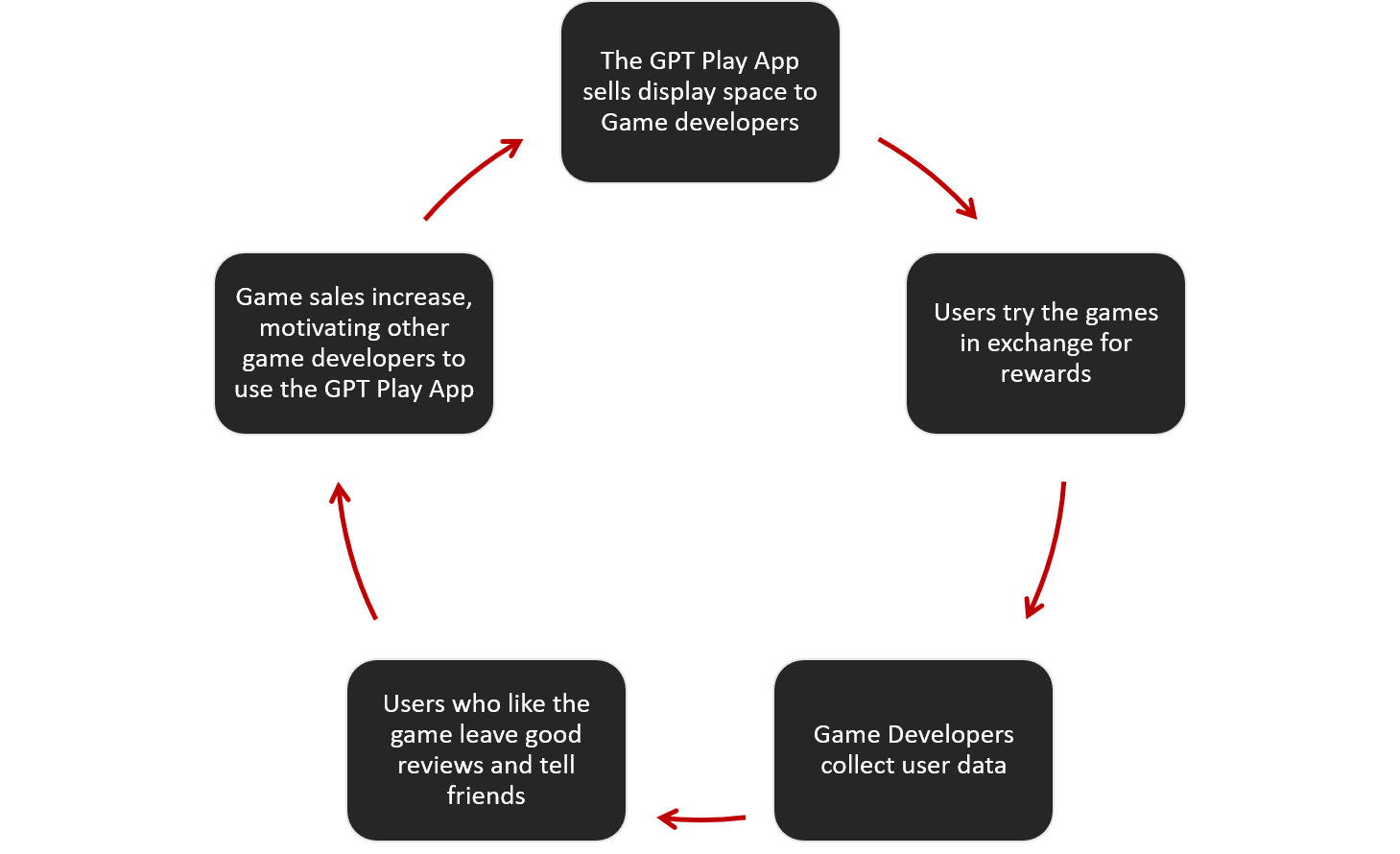
Open Settings and browse to System > Power & sleep. On the right side of this screen, click Additional power settings to open the Power Options menu on the Control Panel.
Here, click Choose what the power buttons do on the left sidebar. You’ll need to provide administrator permission to change the settings on this page, so click the text at the top of the screen that reads Change settings that are currently unavailable.
Now, untick Turn on fast startup (recommended) and Save Changes to disable this setting.
If you don’t see the Fast Boot option, you don’t have hibernation enabled and thus it won’t show up. To enable hibernation, open an administrator Command Prompt or PowerShell window by right-clicking on the Start button and choosing Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin).
Type the following command to enable it, then try to disable Fast Startup again:
powercfg /hibernate on2. Adjust Virtual Memory Settings
Virtual memory is a feature Windows uses to dedicate a part of your hard drive as pretend RAM. Of course, the more RAM you have the more tasks your system can handle at once. So if Windows is close to maxing out true RAM, it dips into virtual memory.
Some users have reported that Windows 10 can change virtual memory settings, causing boot issues. You should thus have a look at your virtual memory settings and see if you can change them to fix the slow boot problem.
Type Performance into the Start Menu and choose the Adjust the appearance and performance of Windows.
Under the Advanced tab, you’ll see the size of the paging file (another name for virtual memory); click Change to edit it.
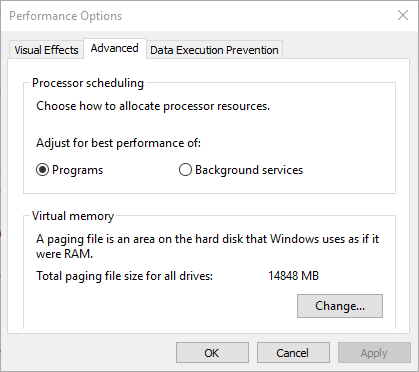
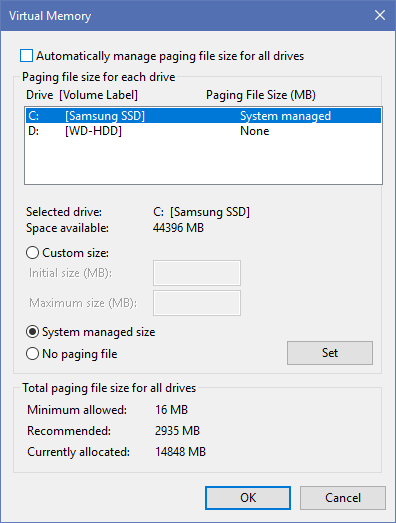
On the resulting window, what’s important is at the bottom. You’ll see a Recommended amount of memory and a Currently Allocated number. Some having this issue find that their current allocation is way over the recommended number.
If yours is as well, uncheck Automatically manage paging file size for all drives to make changes. Then choose Custom Size and set Initial Size and Maximum Size to the recommended value below.
Reboot, and your boot time should improve.
3. Turn Off the Linux Terminal
A while back, Windows 10 got a full Linux bash terminal. This is exciting for developers, but it might also the culprit of your boot issues.
This feature isn’t turned on by default. So if you don’t know what Bash is, you probably don’t need to try this step as you would know if you turned it on.
To turn off the Linux shell, type Windows features into the Start Menu to open the Turn Windows features on or off menu. Scroll down to Windows Subsystem for Linux, uncheck it, and restart.
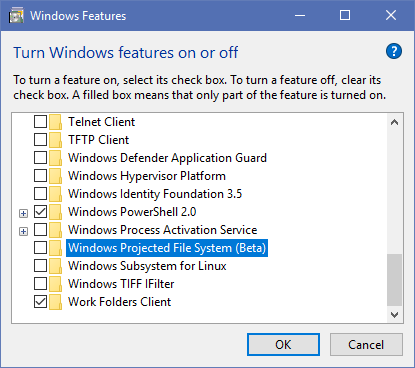
If this fixes your issues, but you need the Linux terminal, you can download other tools to get the Linux command line on Windows.
4. Update Graphics Drivers
Windows 10 is known to mess with drivers, unfortunately. Updating your graphics card drivers can sometimes fixe boot issues, so let’s give it a look.
Open the Device Manager by right-clicking on the Start button and choosing Device Manager. Navigate to Display adapters to see which graphics card you’re using (typically Nvidia or AMD if you have a dedicated graphics card).
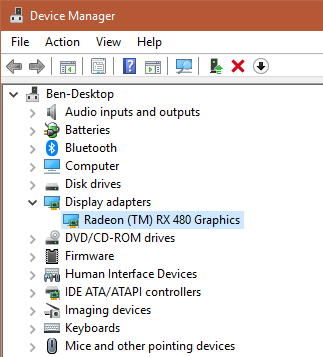
You can usually open the corresponding software on your PC to check for updates. If you don’t have it, you’ll need to navigate to the vendor’s website (or your laptop manufacturer’s website, if you’re using integrated graphics on a laptop) to check for driver updates. Install any new versions available.
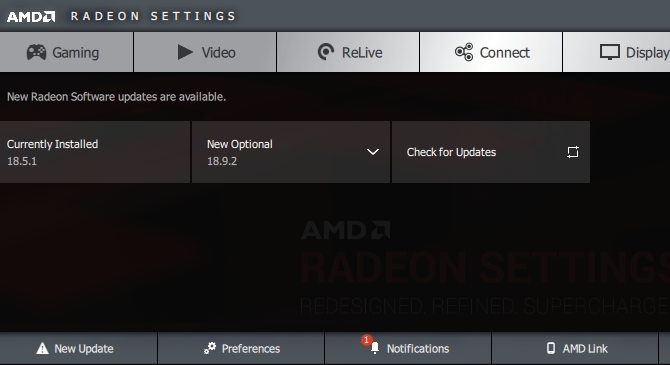
We’ve covered updating your computer drivers in more detail if you need help. Hopefully, an update will fix your issue. It might be worth checking for other driver updates in the Device Manager as well, but we haven’t seen anyone discuss other drivers as a cause of slow booting.
5. Remove Some Startup Programs
Perhaps your slow boot time isn’t caused by one of these issues. If you experience slowness between logging in and actually getting to use your computer, too many startup programs could be the culprit.
A lot of software sets itself to automatically run at startup. If you have dozens of apps loading as soon as you log in, this can really bog your system down right away. Follow our guide to removing heavy startup programs and see if that makes a difference.
6. If All Else Fails, Perform a Reset
If you’ve tried all the above solutions and still can’t speed up your boot time, it might be best to cut your losses and reinstall a fresh copy of Windows 10.
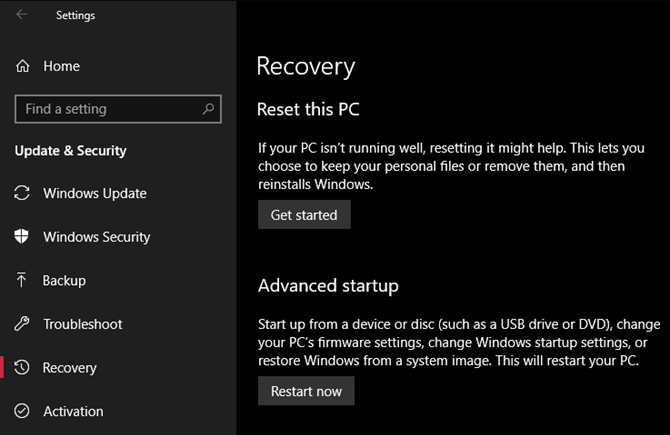
You have several options for resetting your PC. The built-in Refresh option can reinstall Windows without removing any of your files. You’ll should still back up your computer data before this, though.
Head to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery and select Get started under Reset this PC to start.
Slow Booting in Windows 10, Begone
Hopefully, applying one or all of these fixes works for you. Slow startup is a huge pain, but you thankfully have options to combat it. If nothing else works, hold out for the next major Windows 10 release, which should clear up the issue.
Looking for more? Check out our basic troubleshooting guide for Windows and more tricks for speeding up Windows.
Read the full article: 6 Tips to Fix Slow Boot Times in Windows 10