GitHub is a code hosting platform for collaboration and version control. You can work on code with anyone from anywhere. It’s also a platform for the world’s largest developer community.
GitHub provides many features like easy project management with repositories, effective team management using tools like pull requests and issues, easy code hosting, and more. Let’s examine these methods further as we take a look at how to clone a repository using Git Bash.
What Is a GitHub Repository?
A repository is a storage space where all files of a project reside. It’s also commonly known as a “repo.” A GitHub repository is a remote repository where you can store all of your project’s files and each file’s revision history. You can store any type of folder or file like images, HTML files, .css files, .py files, CSV files, excel files, JSON files, etc.
You can create a GitHub repository as Public or Private. By creating a repository as public, anyone on the internet can see that repository. You get to choose who can commit and make changes to that repository, though. Conversely, by creating a repository as Private, you have full control over who can see and make changes to that repository.
Github initializes a repository with a README file, a .gitignore file, and a license file.
A README file lets you write a complete description of your project and include any necessary instructions. A .gitignore file contains the name of the files you don’t want to push to GitHub. Whereas a license tells others what they can and can’t do with your code.
What Does Cloning a Repository Mean?
Cloning a repository means creating a local copy of your GitHub repository. By creating a local copy you can easily add or remove files, fix merge conflicts, and can commit easily. Working on a local copy of the repository provides more flexibility to the users. You can make changes and experiment with the repository safely.
Once you clone a GitHub repository, a full local copy is created along with all versions of every file and folder for the project. You can even clone another person’s existing repository to contribute to a project. After making changes to the repository, you can easily push it to the remote repository on GitHub using Git Bash.
Check if Git and Git Bash Is Installed on Your System
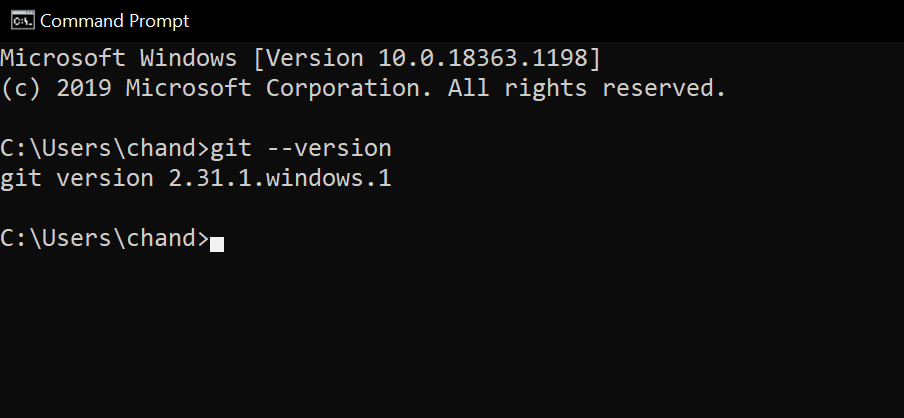
Make sure that you have Git and Git Bash installed on your system. You can check if Git is installed on your system by typing the following command into the Command Prompt:
git --version
The command prompt will display the installed version of Git. To check if Git Bash is installed on your system, press the windows button and search Git bash.

If neither of them are available, follow the correct steps to successfully install Git and Git Bash on your system.
Creating a GitHub Repository
You can create a GitHub repository by following these steps:
1. Go to the official GitHub website.
2. Click the Plus icon from the top right corner and select New repository.

3. A new page will be opened where you’ll have to fill in some details to create a new repository. Enter a short and memorable name for your repo. GitHub also auto-suggests repository names to use for inspiration.

4. If you want, you can provide a short description of your project in the description box. This step is completely optional.
5. Select the repository visibility as Private or Public according to how you want others to see your repository.

6. You can initialize the repository with a README file, a .gitignore file, and a license. According to GitHub, “You can add a README file to your repository to tell other people why your project is useful, what they can do with your project, and how they can use it.”
You can choose a .gitignore file from a list of available templates. Similarly, you can choose a license from the list of available licenses. Adding all these files increases the credibility of the repository.
7. Finally hit the Create Repository button to create a new repository.
Cloning a GitHub Repository Using Git Bash
1. Navigate to the repository you want to clone. You can use this sample repository to try cloning for the first time.
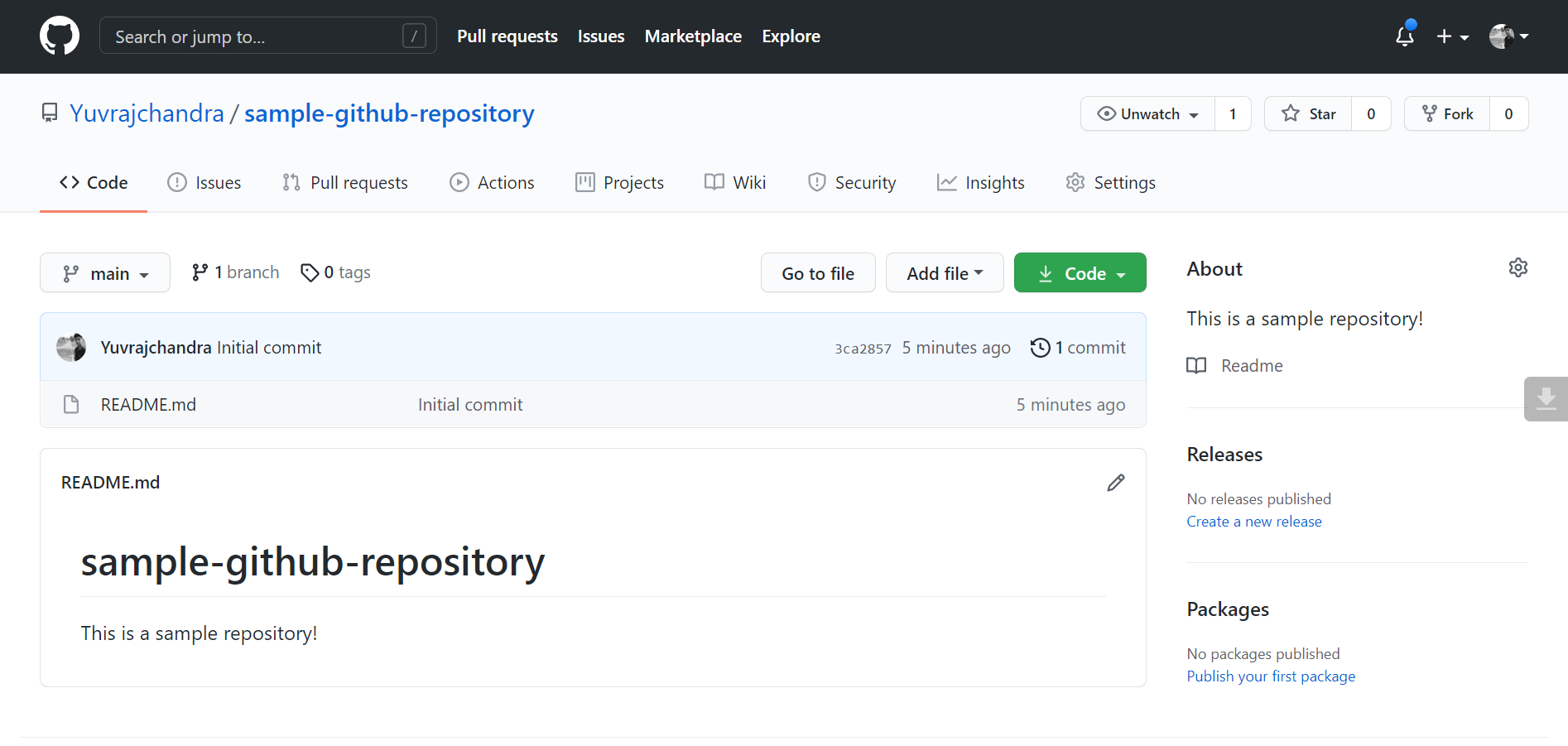
2. Click on the Download Code button.

3. A box will open when you will click the Download Code button. Click on the Copy to clipboard icon to copy the repository URL through the HTTPS method.

4. Open Git Bash.

5. Go to the directory where you want to clone the repository using the cd command.

6. Enter the following command and replace the [REPO URL] with the link that you copied earlier.
git clone [REPO URL]For example, to clone the sample repository that we used earlier, type the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Yuvrajchandra/sample-github-repository.git7. Press enter to have a local copy of the repository on your system.

Other Ways to Download a GitHub Repository
You can also opt for other methods to download a GitHub repository, such as using the GitHub Desktop to clone a repository. GitHub Desktop is an app for Mac and PC users that takes version control from the command line to the desktop. It was created by GitHub to simplify version control.
You can perform all of the same tasks like cloning, deleting, updating, and saving a repo with GitHub Desktop that you can do with Git Bash. Git Bash has a steep learning curve but it is more powerful than GitHub Desktop.
Another simple method to download a GitHub repository is to directly download the ZIP file of the repo. You can follow these simple steps to download a ZIP file of the repository:
- Go to the repository that you want to download. You can use this sample repository to try downloading the ZIP file of the repo for the first time.
- Click on the Download Code button and then click the Download ZIP option. The repository will be downloaded to your system within a few seconds.

Become a Pro-Coder Using GitHub
GitHub provides a platform to share your code with others, create awesome projects, earn badges, and do much more. You can get started by creating your first repository on GitHub.
If you are an experienced programmer, you can contribute to open-source GitHub repositories. Utilize the features of this platform to increase your coding skills and get recognized in the programming community.