Almost every device you can buy today supports Bluetooth, but what is Bluetooth? Simply put, Bluetooth is a way for two nearby gadgets to transmit data to each other.
Let’s take a look at what Bluetooth is, trace its roots, discuss its pros and cons, and find out how it differs from other common wireless technologies like Wi-Fi or NFC.
What Is Bluetooth?
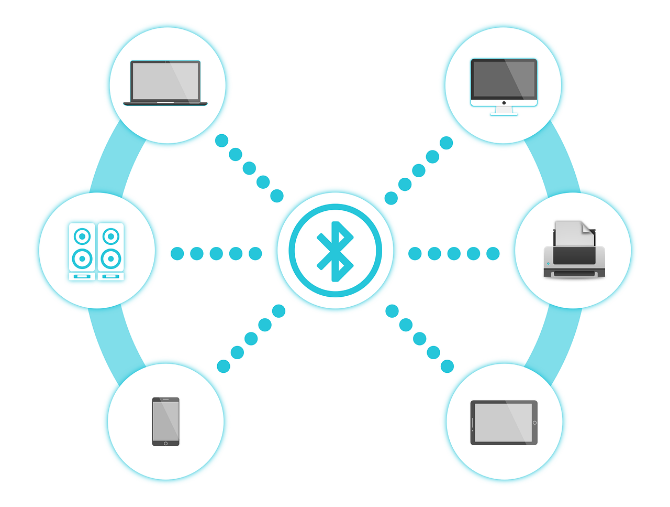
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard whose purpose is to connect gadgets without a cable. The Bluetooth module is a tiny part of the chip in a device, which lets it wirelessly communicate with a Bluetooth module on any other devices.
Generally speaking, Bluetooth is used to transfer small amounts of data while being efficient with battery usage. Among the various wireless standards (like Wi-Fi), Bluetooth is known for maintaining a stable connection in short distances, and transferring small amounts of data without taking too much power. Yes, you can ignore that old Bluetooth myth about it draining your battery life.
Who Invented Bluetooth?
Bluetooth was invented by a team of engineers working for Ericsson, the networking giant. Ericsson’s Dutch electrical engineer Jaap Haartsen is credited as the inventor of Bluetooth. Haartsen has said he developed the standard in 1994, but hadn’t yet found a name for it.
Why Is It Called Bluetooth?

Although Ericsson had invented it, it still needed other companies to adopt Bluetooth across devices. The name actually came from a partner company, Intel, whose employee Jim Kardach suggested it.
Bluetooth is named after the 10th century king of Denmark and Norway, Harald Bluetooth. The king famously united Danish tribes into one kingdom, much like the Bluetooth technology unites communication protocols.
Who Owns Bluetooth Now?

No one “owns” Bluetooth, but its use and advancement is managed by an entity. To ensure Bluetooth became a universal communications protocol, in 1998 a group of companies came together to form the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), a not-for-profit group.
Today, the Bluetooth SIG handles the development of new Bluetooth standards, like Bluetooth 5, and licenses the technology to partners and members. Currently, there are over 30,000 members in the Bluetooth SIG.
How Does Bluetooth Work?

Bluetooth works on radio waves, specifically in the 2.4GHz spectrum. This short-range frequency is commonly used by most appliances that need wireless connectivity, including Wi-Fi routers.
What makes Bluetooth different is the use of a technique called frequency hopping. It’s a bit technical, but there’s a simple explanation. Bluetooth uses 79 bands of radio waves in the aforementioned 2.4GHz frequency. When you send data, Bluetooth first divides this data into smaller packets. These packets are sent individually over those 79 bands, and Bluetooth is smart enough to change bands rapidly so that no one line gets clogged.
That’s the main platform of the technology. With the smart “hopping” of data transfers, Bluetooth can simultaneously connect up to eight devices and allow them to talk to each other.
Does Bluetooth Use Data?
This is a commonly asked question, especially since Bluetooth’s competitor Wi-Fi is associated with internet connections. The short answer is No! Bluetooth does not use any data.
When Bluetooth connects two devices, it forms something called a Personal Area Network (PAN). PAN does not require an internet connection or mobile service to transfer files or anything else.
The Specifics of Bluetooth

You can roughly divide Bluetooth into Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate (BR/EDR) and Low Energy (LE). The difference between these was more necessary a few years ago, but it’s not something you need to concern yourself with anymore. Most devices bought in the five or so years come with Bluetooth 4.0, 4.1, or 4.2—all of which make Low Energy the priority.
This process of breaking down data into smaller packets and sending them individually is also why Bluetooth is used mainly for small data transfers that don’t need to happen quickly. If you need to transfer large amounts of data quickly, there are better wireless protocols than Bluetooth.
Specifically, Bluetooth 4.2 can send data at up to 1Mbps, which will increase to 2Mbps with Bluetooth 5. The distance between devices is about 11-16 yards with Bluetooth 4.2, which will go up to 44 yards with Bluetooth 5.
What Is the Difference Between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi?

Technically, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are both wireless standard protocols to let two devices connect without cables. But each technology’s merits and application are different.
Wi-Fi is a stronger and faster connection, which takes more battery. Bluetooth’s focus is on battery efficiency. A side effect of this is that Bluetooth actually maintains a more stable connection, since it interferes less with the same 2.4GHz radio waves that Wi-Fi and other wireless radio signals use.
While Bluetooth is generally the better technology to use for simple, low-power connections between two devices, you can also connect two devices with Wi-Fi Direct. Check out more about the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct.
Does My Computer or Laptop Have Bluetooth?

Bluetooth is a common and mass-used technology which you will find on most smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other wireless consumer devices.
This gets a little more tricky with desktop computers. Some motherboards do come with Bluetooth built-in, but it’s not that common. Have a look at how to set up Bluetooth on Windows 10. If you find your PC doesn’t have it after following those steps, you can add Bluetooth to your computer.
Is Bluetooth Safe?

No technology is fully safe, and the matter only gets more complicated when you’re dealing with something like Bluetooth. Bluetooth places a premium on making it easy to pair two devices, and that’s a double-edged sword as miscreants can exploit this ease to cause harm.
Over the years, security experts have discovered several risks in Bluetooth. The latest big vulnerability was found in 2017, called BlueBorne. The Bluetooth SIG ensures these are patched in good time. But that said, there are a few steps you can take for a little extra security:
- Change your Bluetooth’s four-digit PIN. It’s usually a simple procedure depending on your device. The most common default PIN is 0000 and hackers know this, so when you can, change it.
- Switch off Bluetooth when you aren’t using it. It’s the safest change you can make, and using “hidden profiles” and other such tricks have proven not to increase security.
Bluetooth: More Than Phones and Speakers
Now that you know about the technology, and how to stay safe while using it, it’s time to get it working on your gadgets. The most common use of Bluetooth is to connect a phone to Bluetooth speakers or headphones. But there’s a lot more you can do with it.
In fact, if you fancy a bit of DIY tech, you can create a wireless message board for almost no cost. If you car stereo doesn’t have Bluetooth, it’s easy to add it in. And then there’s the ultimate dream of a Bluetooth-powered remote controlled car. For all these and more, check out our selection of the best DIY Bluetooth projects for tech geeks.
Read the full article: What Is Bluetooth? 10 Common Questions, Asked and Answered