If you’ve ever seen the “Windows has detected an IP address conflict” message, you might wonder what this message means. While IP conflict issues aren’t usually difficult to fix, they are confusing, especially for those new to networking.
Let’s look at what an IP address conflict is, how they happen, and the steps to fix this error when it pops up.
What Is an IP Address Conflict?

An IP address conflict occurs when two or more devices on the same network are assigned the same IP address. To explain why this is a problem, we must take a step back and look at what IP addresses are for.
Like a physical home address for receiving mail, IP addresses act as a way to identify your computer on a network. Your router uses those IP addresses to direct network traffic to the right devices. Check out our full guide to home networking for more details on this.
Because of this system, each IP address cannot be assigned to more than one device. If this happens, the network becomes confused by the duplicate IP addresses and can’t use them correctly. But since two computers cannot have the same IP address, how does the IP error occur?
How Does an IP Address Conflict Happen?
Under most circumstances in modern networks, IP conflicts are rare. This is because of DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), a system that routers use to hand out IP addresses.
With DHCP, when you connect a new device to your network, your router chooses an available IP address from the pool of options. The device uses this IP for some time, until the lease expires and it has to get a new one. Unless your router malfunctions, two devices should never get the same IP address from this system.
More commonly, an IP conflict can occur when you assign static IP addresses on your network. Instead of DHCP automatically choosing an address, you can set up a network device to always use the same IP address that you specify. If you mistakenly assign the same static address to two devices, you’ll run into a duplicate IP error.
Another IP conflict scenario can occur if you have two DHCP servers on your network (which you should avoid). For example, you might have your own wireless router connected to your ISP’s modem/router combo. If both devices are trying to act as a router, they might hand out duplicate IP addresses.
Finally, you can introduce duplicate IPs onto your network when a machine comes back online after being in standby mode. For instance, say you leave your laptop in a hibernated state for two weeks. During that time, your router may recall the laptop’s IP address and assign it to another device, like your phone.
When you turn the laptop back on, it may think it still owns that IP address, which results in an IP conflict. This may also occur if you put your computer in standby on another network that uses the same IP pool as yours.
How to Fix IP Address Conflicts
Like all network troubleshooting, the first step you should take is restarting the affected computer and your networking equipment.
The IP address error could have been a small glitch, which a reboot will resolve. Restarting your router and/or modem will re-assign all IP addresses via DHCP.
Troubleshooting Static IP Addresses on Windows
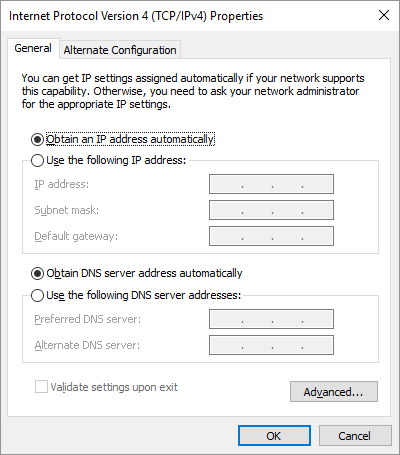
If restarting everything doesn’t work, the problem is a little deeper. You should next check to see if your computer is using a static IP address. On Windows, open Settings and go to Network & Internet > Status. Click Change adapter options on this menu, then double-click the name of your network connection.

On the resulting screen, click Properties, followed by double-clicking Internet Protocol Version 4. This menu should have Obtain an IP address automatically selected. If it isn’t, select the automatic option instead and hit OK. Repeat these steps for Internet Protocol Version 6 and see if the conflict goes away.
You should also try releasing your computer’s current IP address and obtaining a new one. Restarting also accomplishes this, but it’s still worth a try at this time. To do so, right-click on the Start button and select Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell. Type the following command to give up your current IP, followed by Enter:
ipconfig /releaseAfter this, use the following command to obtain a new IP address from the router:
ipconfig /renewTroubleshooting Static IP Addresses on macOS
On a Mac, you’ll find IP address options under Apple menu > System Preferences > Network. Select the connection type you’re using from the left side, then click Advanced.
On the resulting page, select the TCP/IP tab. If the Configure IPv4 box is set to Manually, change it to Using DHCP. Check that Configure IPv6 is also set to Automatically, then hit OK.

To refresh your current IP on a Mac, click the Renew DHCP Lease button to the right on this page.
Check Your Router for Conflicting Devices
If the above steps didn’t fix the issue, you should next log into your router’s administration panel and take a look at the connected devices. How you do this will depend on your router model, so we can’t give exact instructions. Have a look our router management intro guide for help understanding the interface.
Typically, you’ll find a list of connected devices under a section titled Attached Devices, Connected Devices, My Network, or similar. Have a look at each device and keep an eye out for duplicate IP addresses. To help narrow this down, you can check the IP address of your computer by typing ipconfig into a Windows Command Prompt or ifconfig into the Mac terminal.

If you find two devices with the same address, remove any static IP address settings or refresh their IPs in your router to resolve the conflict.
Update Your Router Firmware
A faulty router can cause IP conflicts to occur frequently and without warning. If you continue to have IP address errors even after performing the above troubleshooting, you should update your router’s firmware.
The exact steps to this also depend on the router you have. Usually, you’ll find a Firmware Update option when you log into your router’s admin panel. This may be under an Advanced or Tools menu.
While some routers let you update the firmware automatically through the panel, others require you to download a file from the manufacturer and upload it to your router. Check your router maker’s website for more help.
Resolve IP Address Conflicts Peacefully
Now you know what an IP address conflict is, how two devices could get the same IP address, and how to fix IP conflicts. Most of the time, a conflict won’t occur on the average home network. And if it does, you can often resolve it with a few quick reboots.
For more help with IP problems, have a look at how to fix the “Wi-Fi doesn’t have a valid IP configuration” error.
Read the full article: What’s an IP Conflict and How Do You Resolve It?



